Where does life lurk under the ice of Antarctica? The answers keep surprising us. In January, for example, researchers found corals, sponges and even giant sea spiders some 750 feet under the waves — all suddenly unearthed when a glacier broke free during a Schmidt Ocean Institute voyage.
The find is hardly unusual; in 2021, another team uncovered sponges and other species underneath nearly 3,000 feet of ice in the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf — the first time any living creatures had been found there. But with global heating and climate change wreaking havoc on the ice caps of Antarctica, researchers are looking to a new map of the south polar region to better map global warming changes and their effects on subglacial life. These efforts won’t just inform how to protect these fragile ecosystems — they could act as a sort of road map for finding alien life on other worlds.
Sharper satellite images helped form the backbone of Bedmap3, which updates maps of icy Antarctica — particularly among the high mountains and isolated interior of the eastern part of the continent. As the name Bedmap3 implies, this is the third map of Antarctica produced by a group led by the British Antarctica Survey (BAS); the first was done in the early 2000s.
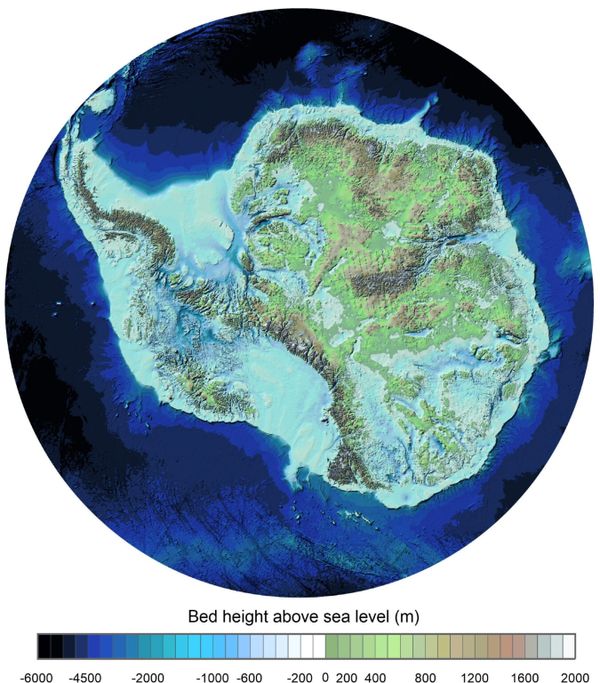 Bedmap3 reveals new insights into the topography of Antarctica. From Bedmap3 updated ice bed, surface and thickness gridded datasets for Antarctica (by Pritchard, H., et al. )
Bedmap3 reveals new insights into the topography of Antarctica. From Bedmap3 updated ice bed, surface and thickness gridded datasets for Antarctica (by Pritchard, H., et al. )
As we better map isolated and icy areas on Earth, these findings also help inform where life not only can form, but thrive. Glacial-crusted moons dot our solar system near the giant planets, most famously watery Europa near Jupiter and the fountain-spouting Enceladus near Saturn. In October, NASA launched Europa Clipper, a probe that will travel 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers) and survey the Jupiterian moon. In a release, NASA said Europa Clipper would fly-by just 16 miles from the surface, equipped with “ice-penetrating radar, cameras, and a thermal instrument to look for areas of warmer ice and any recent eruptions of water.”
"The more we know about Earth's icy environments, the better we will be able to understand the other environments."
But it won’t arrive until 2031 and that’s only one icy world that could be home to life — most recently, it was reported that Miranda, a moon of Uranus, might be another candidate for extremophile life that can flourish under intense cold. We'll need far more spacecraft to figure out if anything living lies under the crust of these worlds, but in the meantime, Antarctica serves as a handy analog to figure out the limits of life.
"The more we know about Earth's icy environments, the better we will be able to understand the other environments," said Robin E. Bell, referring to icy moons. Bell is a research professor at Columbia University who has led 10 expeditions to Antarctica and Greenland in part to study deep subglacial lakes.
While not involved in Bedmap3, Bell said the study holds potential: its higher resolution will show how "the water clearly pulses between the smaller lakes, and flows uphill in the Gamburtsev Mountains, until it is refrozen to the ice sheet base," she said.
Want more health and science stories in your inbox? Subscribe to Salon's weekly newsletter Lab Notes.
That's because Bedmap3 bumps up the resolution of imaging from space – after all, satellites have much improved over the decades – as well as better defining the edge of where the ice meets the sea, Peter T. Fretwell, a BAS geographic information officer, told Salon.
Fretwell was second author on a scientific paper published last month in Scientific Data describing Bedmap3's results. Each grid square on the map has a resolution of a third of a mile in length, which is a substantial improvement from Bedmap2, he noted. On that map, some of the more isolated areas had a resolution of just three miles by three miles.
The community is already working on lake databases and hydrological models based on the Bedmap3 results, and anticipates using this information for ice sheet modeling, geology and better simulations of how the environment used to behave in the ancient past, Fretwell said. "We hope that these new datasets will be out shortly," he added.
 Removing the 27 million cubic km of ice that covers Antarctica, the hidden locations of the tallest mountains are revealed. From Bedmap3 updated ice bed, surface and thickness gridded datasets for Antarctica (by Pritchard, H., et al. )
Removing the 27 million cubic km of ice that covers Antarctica, the hidden locations of the tallest mountains are revealed. From Bedmap3 updated ice bed, surface and thickness gridded datasets for Antarctica (by Pritchard, H., et al. )
While Fretwell cautioned he is not an expert in lacustrine habitats, meaning large bodies of water where life may be possible, he said Bedmap3 will help inform new studies of subglacial lakes. The community will be meeting soon to go over the results, he added: "One thing that is planned is a meeting in May to look at how we go forward with future glaciological survey following on from Bedmap3."
Bell is already excited for the potential, after having led teams that found a volcano underneath the west Antarctic ice sheet and that spotted several lakes embedded in ice roughly two miles thick. She said the satellites and aerial surveys that created Bedmap3 will allow researchers to better estimate how thick the ice is, particularly in transient zones where the grounded ice changes to a floating ice shelf.
We need your help to stay independent
"Our knowledge of subglacial lacustrine environments has hinged largely on satellite measurements and radar mapping," Bell said, noting that the under-ice Lake Vostok – first suggested by Soviet sounding studies in the 1950s and 1960s – was at last confirmed in 1993 using laser altimetry from the European Remote Sensing-1 satellite.
Lake Vostok is roughly 34 million years old, but Bell is among the researchers who have suggested water circulated through the microbe-filled lake roughly every 50,000 years. When Bell's study was published in 2002, the researchers noted the ice sheet and the lake depend on one another; the circulation of the lake is controlled by the ice sheet thickness, and the cycle of freezing and melting at the base of the ice controls changes in water, sediment and life.
Large and small lakes alike are therefore largely affected in the zone "where the base of the ice sheet melts and where that meltwater flows," Bell said. She expects Bedmap3 will help improve the existing ice sheet models and help researchers better understanding how water flows under the thick ice of Antarctica. And perhaps, even faraway moons.



Shares